What Is Sonography Technician Training?
Published - May 14, 2025
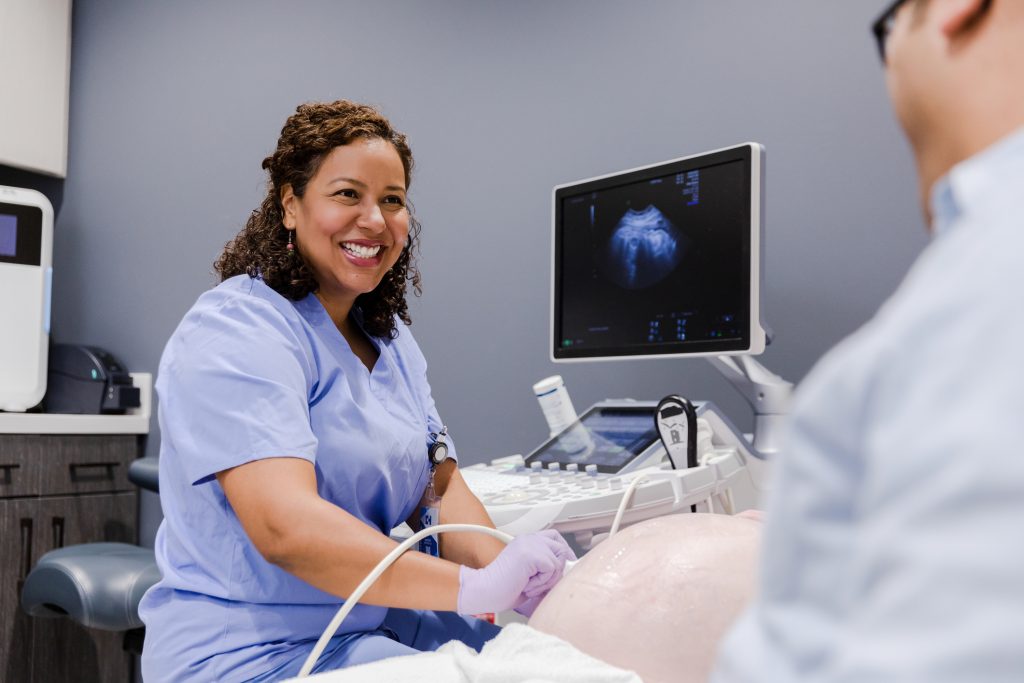

Many people want to work in healthcare because they can make a difference in the lives of others. If you’re going to work in healthcare but don’t want to perform venipuncture or other medical procedures, consider becoming a sonographer. What you do as a sonographer is meaningful and can help doctors and nurses make better treatment decisions. So, what is sonography technician training?
What Is Sonography Technician Training?
Sonography technician training teaches you how to use ultrasound technology to capture real-time human body images. Sonographers work closely with patients and medical teams in hospitals, clinics, imaging centers, and OB/GYN offices.
Sonographers are Important
Sonographers can recognize unhealthy tissue, alerting the doctor if necessary. Their work leads to early detection of severe conditions like cancer, heart disease, or high-risk pregnancies. For example, a sonographer might help confirm internal bleeding in emergency rooms. They may be the first to spot a baby’s heartbeat in prenatal care. Their accuracy and attention to detail help doctors make the best decisions for better health outcomes.
What Do You Learn During Sonography Technician Training?
Sonography technician training programs prepare you to work with patients and perform diagnostic ultrasound scans. Training combines medical knowledge, technical skills, and hands-on practice.
Patient Care Fundamentals
One of the first areas you will focus on in the sonography technician training program is patient care. Sonographers must know how to prepare patients for procedures and position them correctly for accurate results.
Medical Terminology and Ethics
Sonography technician training includes how to speak and chart using medical terms, as well as how to maintain patient privacy and professionalism.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
Diagnostic imaging teaches you to use ultrasound equipment to capture clear, accurate images. You will practice scanning techniques and learn to adjust equipment settings to improve image quality. Programs also teach you to recognize abnormal features and follow imaging protocols for different body systems.
Anatomy and Physiology
During these sonography technician courses, you will study the structure and function of organs, muscles, tissues, and blood vessels. You also learn how different diseases affect the human body. This helps you recognize what looks abnormal and what may need further review by a doctor.
Physics of Ultrasound
You are trained in the science behind ultrasound technology. This includes how sound waves move through the body and how wave frequency affects image detail. Understanding ultrasound physics helps you troubleshoot issues and improve scan results.
Equipment Operation
Training includes using different types of sonography equipment and adjusting machine settings. Hands-on training and clinical rotations help you gain experience and build confidence.
Clinical Rotations
Sonography technician training programs include real-world training at local hospitals or clinics. During clinical rotations, you will work under supervision while performing sonography duties.
How To Become a Sonography Technician
Becoming a sonography technician takes training and hands-on experience. Here’s a step-by-step process of becoming a sonography technician.
Step #1: Graduate from High School or Earn a GED
The first step in becoming a sonography technician is completing high school or earning a GED.
Step #2: Meet Program Prerequisites
Prerequisites may include:
- A background in science or healthcare
- Minimum GPA (often 2.5 or higher)
- CPR certification
- Possibly a background check or drug screening
Step #3: Choose the Right Sonography Program
There are two main types of sonography degrees:
Associate Degree (2 years): includes core sonography courses, lab practice, and clinical training. It qualifies you for entry-level jobs in hospitals or imaging centers.
Bachelor’s Degree (4 years): This offers more advanced study. It may lead to supervisory roles or specialties like cardiac or vascular sonography. A bachelor’s degree is also helpful for moving into healthcare management or education later.
Both programs must include hands-on clinical hours and be accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP).
Step #4: Complete Clinical Training
During the program at CBD College, you will work in real healthcare settings. Clinical training helps you apply what you’ve learned in the classroom with patients under the guidance of industry experienced instructors. This is required for graduation and certification.
Step #5: Get Certified
After graduation, employers require certification. CBD College helps you prepare for the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) exam. To take this test, you must meet education and clinical requirements. Passing the exam proves you’re qualified to work as an entry-level sonographer.
What To Look for in a Sonography Technician Training Program?
Choosing the right sonography training program is essential to becoming a certified medical imaging professional. Here is what you should look for in a sonography technician training program:
Accreditation by CAAHEP
The program should be accredited by an organization like the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP). CBD College’s sonography programs meet national medical imaging education and training standards.
Why does this matter? Graduating from a CAAHEP-accredited program makes you eligible to sit for the ARDMS (American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography) exam. Without CAAHEP accreditation, your certification path becomes more difficult and may require additional work experience or alternative credentials.
In-Person Clinical Rotations
Look for in-person clinical training programs at hospitals, clinics, or imaging centers. Sonography is hands-on, and classroom learning only supplements in-person clinical training. Clinical rotations give you real-world experience working with patients and medical staff using ultrasound equipment.
For example, you might spend a rotation at a hospital OB/GYN department where you assist with prenatal scans. You will learn how to position the patient, select the correct transducer, adjust machine settings, and capture clear images for the physician.
Hands-On Lab Training
In addition to clinical rotations, a good program offers hands-on training where you practice scanning techniques. This allows you to apply your knowledge before entering a clinical setting.
What is The Difference Between an Associate’s vs a Bachelor’s Degree in Sonography?
Both associate and bachelor’s degrees in sonography can lead to a successful career, but they offer different timelines, costs, and career outcomes.
Program Length
An associate’s degree in sonography takes 2 years to complete. You will be ready to start scanning in real clinical settings in under 20 months at CBD College.
A bachelor’s degree takes 4 years. It includes more general education courses and advanced sonography topics. It may also offer specializations like cardiac, vascular, or pediatric sonography.
Cost
An associate program requires fewer credits and less time, which means lower tuition costs and a quicker entry into the workforce. This makes it a good way for you to complete your education without long-term debt.
A bachelor’s degree costs more due to the longer length of study. However, some employers offer tuition reimbursement or incentives for advanced education, especially in hospital systems.
Career Opportunities
An associate degree qualifies you for entry-level sonographer jobs in hospitals, imaging centers, and OB/GYN clinics. You will be ready to take the ARDMS certification exam and start working immediately.
A bachelor’s degree may open doors to management, education, or specialized roles, such as echocardiography or research. It can also make you more competitive for large hospitals or academic medical centers positions.
Advantages of Pursuing a Bachelor’s Degree in Sonography
A bachelor’s degree in sonography opens doors to leadership and specialization. While associate degrees provide a quicker path to become a sonographer, a bachelor’s program can offer additional opportunities.
Expanded Career Prospects
A bachelor’s degree qualifies you for more advanced roles. Some employers prefer candidates with four-year degrees for senior positions. For example, some graduates become lead sonographers, clinical supervisors, or training coordinators. Others use their degree to move into roles teaching future sonographers or managing imaging departments.
Advanced Learning Opportunities
Bachelor’s programs go beyond basic ultrasound training. You will take advanced courses on cross-sectional anatomy, research methods, healthcare ethics, and patient safety. This program may also include training in health informatics or medical leadership.
Specializations
Bachelor’s programs can offer more specialized roles. These can include:
- Cardiac sonography (echocardiography)
- Vascular technology
- Musculoskeletal sonography
- Pediatric or fetal echocardiography
What is the Difference Between an Online vs In-Person Sonography Program?
Sonography training includes both technical knowledge and hands-on skills. That’s why most programs are offered in in-person or hybrid formats. However, each format offers different benefits.
Online Learning
Online sonography programs can offer more flexibility. Online programs allow you to complete general coursework, like ultrasound physics, medical terminology, anatomy, and patient care theory, through online lectures, quizzes, and discussion boards. However, online programs cannot provide clinical training, which is required to sit for the ARDMS exam. Without in-person clinical hours, you won’t qualify for certification.
In-Person Programs
In-person programs on campus offer direct access to ultrasound machines, scanning labs, and instructors. You get immediate feedback while learning to perform scans, use transducers, and capture accurate images.
Hybrid Programs
Hybrid programs combine online coursework with required in-person labs and clinical training. You can complete lecture-based classes like ultrasound theory, healthcare ethics, or cross-sectional anatomy virtually. Then, you attend labs and clinicals to practice scanning and patient care. The hybrid format offers the flexibility of online learning while still meeting the clinical requirements set by CAAHEP and ARDMS.
Do I Need Certification to Become a Sonography Technician?
Yes, certification is essential to work as a sonography technician. Most employers require it. Certification proves you’ve met national standards in both technical skill and medical knowledge.
How To Get a Sonography Technician Certification
Certification involves completing an accredited education program, gaining clinical experience, and passing a national certification exam.
Step #1: Graduate from a CAAHEP-Accredited Sonography Program
The first step to certification is enrolling in a sonography training program accredited by the CAAHEP. These programs may offer an associate’s or bachelor’s degree, including classroom courses, hands-on lab training, and clinical rotations in real medical settings. Only graduates from these accredited programs qualify for the ARDMS exam without needing extra work experience.
Step #2: Complete Clinical Experience
During your program, you must complete supervised clinical rotations. These occur in hospitals or imaging centers and let you practice with real patients. Clinical hours help build confidence and count toward eligibility for the ARDMS exam.
Step #3: Apply for the ARDMS Certification Exam
Once you’ve completed your program, you can apply for the ARDMS exam. Most sonographers start with the Sonography Principles and Instrumentation (SPI) exam. You must pass the SPI and one specialty exam to earn your certification.
Step #4: Study for the Exam
Use a structured study plan. Focus on anatomy and cross-sectional views, ultrasound physics and, instrumentation, patient safety and scan protocols, and practice exams and flashcards.
Step #5: Pass the Exam and Get Certified
After passing the SPI and a specialty exam, you’ll receive your RDMS credential (Registered Diagnostic Medical Sonographer), depending on your specialty.
Step #6: Maintain Your Certification
To keep your certification, you must:
- Pay an annual fee to ARDMS
- Earn 30 CME (Continuing Medical Education) credits every three years
- Stay updated on best practices, new tech, and clinical guidelines
MRI Technician Program
If you enjoy the idea of working side-by-side with physicians and radiologists and enjoy a good challenge in a technologically advanced field, this is your career choice!
In as little as 18 months, the AAS in MRI Program that follows the ARRT Primary Pathway will prepare you with the knowledge and skills you will need to fulfill the responsibilities of a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technologist.
Contact us now to learn more.
